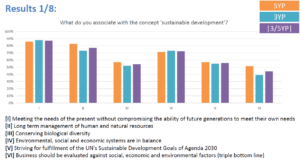
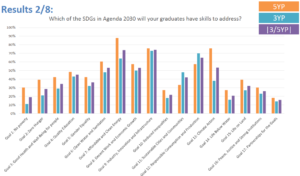
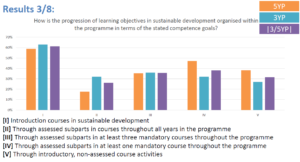
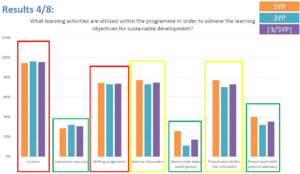
Education for sustainable development (ESD) is becoming increasingly important as we strive to create a more sustainable future for all. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in order to effectively integrate ESD into the education system. These challenges include a lack of understanding of the concept of sustainability, a lack of resources and support for ESD, a lack of integration of ESD into the curriculum, a lack of teacher training, a lack of student engagement, a lack of assessment and evaluation, and a lack of collaboration and partnerships.
1. Lack of understanding of the concept of sustainability:
Many people, including educators, still lack a clear understanding of what sustainability is and why it is important. This can make it difficult to integrate ESD into the education system, as educators may not fully understand the concept and its relevance. To address this challenge, educators and decision-makers need to be provided with clear and accessible information on the concept of sustainability and its importance.
There are many resources that can be useful to raise knowledge and awareness in sustainable development among educators. For example, Unesco has published a set of suggestions for learning objectives for the Sustainable Development Goals of the Agenda 2030.
2. Lack of resources and support for ESD:
Another challenge is the lack of resources and support for ESD. This can include a lack of funding, a lack of materials and resources, and a lack of support from decision-makers. To address this challenge, it is important for educators and decision-makers to advocate for increased funding and support for ESD. This can include lobbying for more funding for ESD programmes and initiatives, as well as developing partnerships with organizations and businesses that can provide resources and support.
This is a subject that is often discussed and debated in various forums. Unesco has also produced a roadmap for ESD that is very informative, and that can be incredibly useful background material when advocating for increased ESD support.
3. Lack of integration of ESD into the curriculum:
A third challenge is the lack of integration of ESD into the curriculum. This can make it difficult for educators to effectively teach ESD, and for students to understand the relevance of the topic. To address this challenge, it is important for ESD to be integrated into the curriculum at all levels of education. This can include developing ESD-specific curriculum and resources, as well as integrating ESD into existing subjects and courses.
Snowflake Education has developed several learning packages for sustainability that can easily be integrated in any course or education programme.
4. Lack of teacher training:
A fourth challenge is the lack of teacher training on ESD. This can make it difficult for educators to effectively teach ESD, as they may not have the knowledge and skills necessary to do so. To address this challenge, it is important for teachers to receive training on ESD, including on the concept of sustainability, teaching strategies, and the use of ESD-specific resources and materials.
Snowflake Education offer a great faculty/teacher training course called Teaching Sustainability in Higher Education – from Theory into Practice.
5. Lack of student engagement:
A fifth challenge is the lack of student engagement in ESD. This can make it difficult for students to understand the relevance and importance of ESD, and to take action to promote sustainability. To address this challenge, it is important to develop engaging and interactive ESD resources and activities that will capture students’ interest and inspire them to take action.
Educational classroom games (board games, simulation games, roleplay games and so on) have shown a strong ability to raise student engagement in the learning process, especially in ESD. I had the opportunity to contribute in a project on critical evaluation of simulations and games as tools for expanding student perspectives on sustainability, for which we reported the findings in this conference paper.
6. Lack of assessment and evaluation:
A sixth challenge is the lack of assessment and evaluation of ESD programmes and initiatives. This can make it difficult to determine the effectiveness of ESD and to identify areas for improvement. To address this challenge, it is important to develop and implement assessment and evaluation tools that can be used to measure the effectiveness of ESD programmes and initiatives.
This research paper by G. Davis (2007) delves deeper into the importance of assessment and evaluation in sustainability, specifically in the field of engineering education. The study was performed at the University of Bristol in Bristol, England, and clearly show that even though students had a good knowledge of the terminology associated with sustainable development principles, there was a discrepancy in the understanding of the various subject areas, tools and methods for sustainable development.
7. Lack of collaboration and partnerships:
A seventh challenge is the lack of collaboration and partnerships between educators, decision-makers, and organizations and businesses. This can make it difficult to effectively implement ESD and to secure the resources and support necessary for its success. To address this challenge, it is important to develop partnerships and collaborations between educators, decision-makers, and organizations and businesses that can provide resources and support for ESD.
A few years ago, Comenius (the EU programme for schools) produced this report. The conclusions in the report generally still hold and this is a great resource for digging deeper into the subject of collaboration and partnerships for ESD.
In conclusion, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in order to effectively integrate ESD into the education system.